|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Dimensions |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Dimensions |
  
|
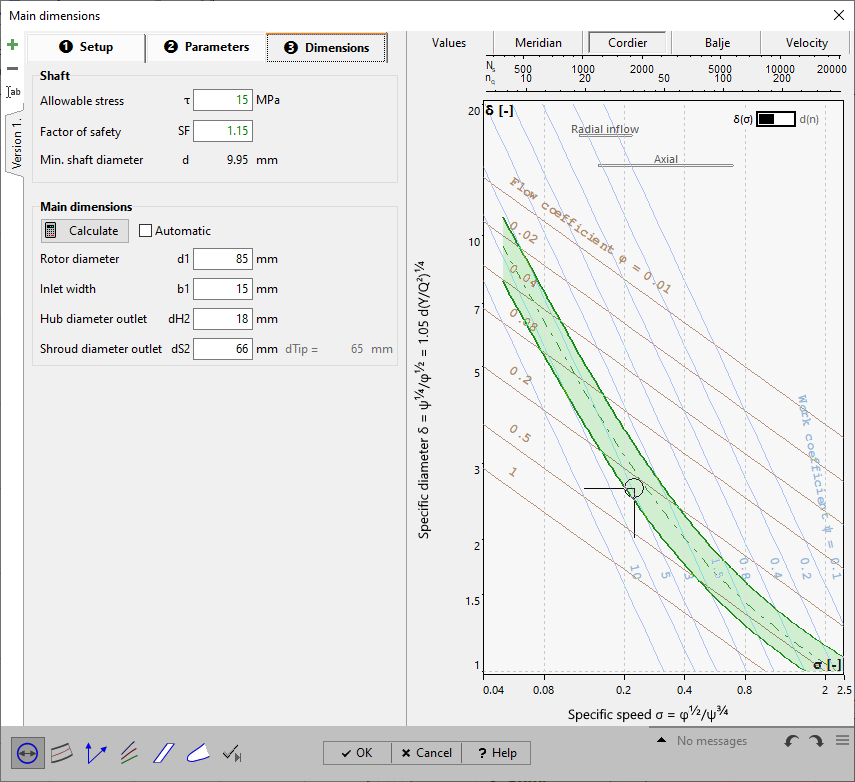
In the panel Shaft, the required shaft diameter is computed.
¢ Shaft/ Hub
The main dimensions can be seen on Main dimensions panel. They can be recomputed by pressing the Calculate-button. The computation is based on "Euler's Equation of Turbomachinery", on the continuity equation and the relations for the velocity triangles as well as on the parameters given in the tab sheets Setup and Parameters.
Individual main dimensions can be calculated separately using the button inside the value field.
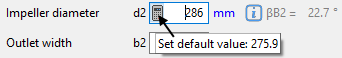
You may accept the proposed values or you can modify them slightly, e.g. to meet a certain normalized diameter.
In case the checkbox Automatic is activated a new calculation will accomplished after any change of parameter. Then the manual alteration of the main dimensions is not possible.
Neighboring components
In specific cases the dimensions of the neighboring components at inlet and/ or outlet can be used to get exactly matching geometry.
![]()
This feature is available only for explicitly uncoupled components or side-by-side impellers.
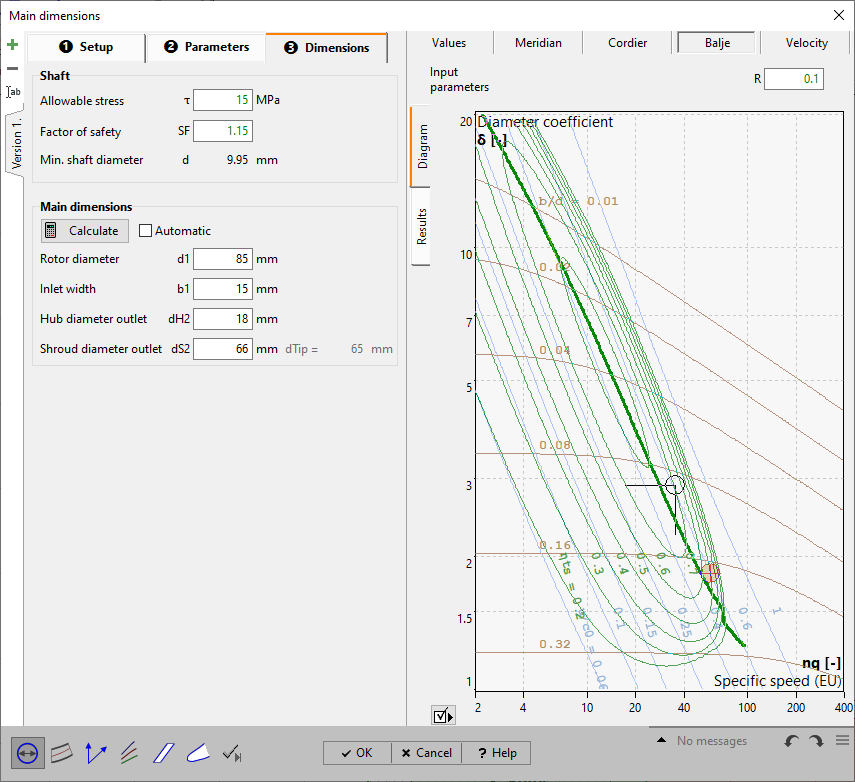
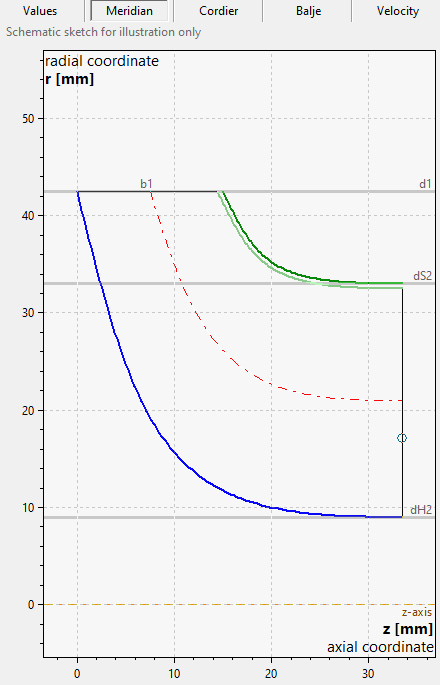
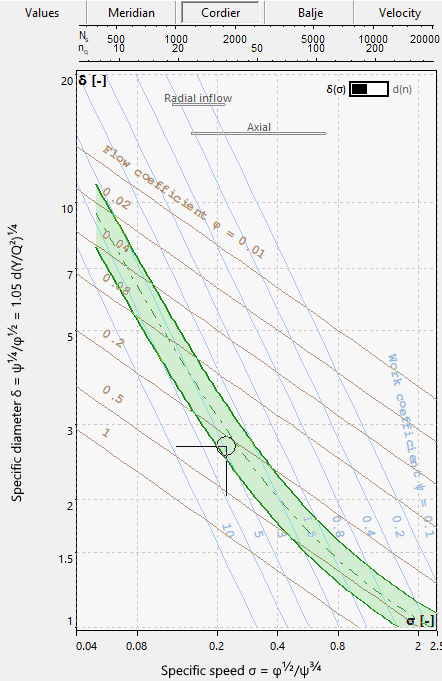
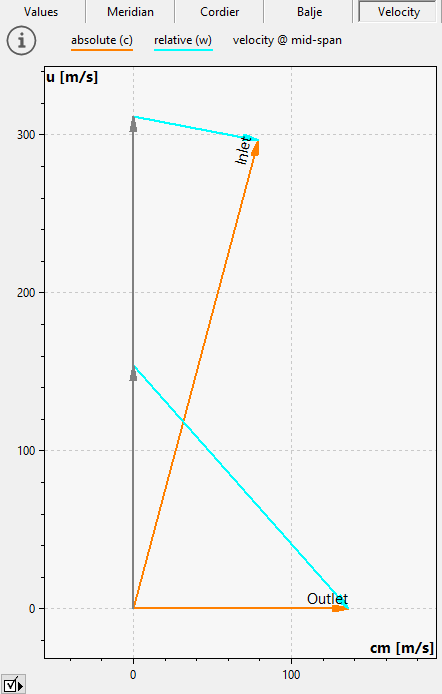
In the right panel of any tab sheet an information panel is situated, which holds the computed variables in accordance to the actual state of design, the resulting Meridional section as well as the Cordier-Diagramm with the location of the best point. These three sections can be chosen by the appropriate soft buttons in the heading.
In the Value section the following variables are displayed for information which result from calculated or determined main dimensions:
Flow properties at: |
density ρ |
Velocity triangles at: |
velocities u, cm, cm*, cu, c, wu, w |
Work coefficient |
|
Flow coefficient |
|
Meridional flow coefficient |
|
Specific diameter |
|
|
Peripheral speed at inlet |
|
|
Machine Mach Number |
|
|
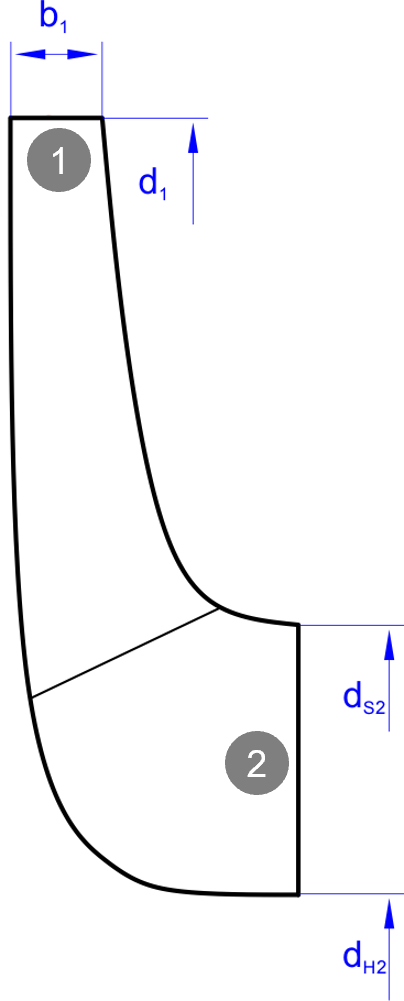
Blade width at inlet |
|
|
Peripheral speed at outlet |
|
|
Mean diameter at outlet |
|
|
Width at outlet |
|
|
b1/d1 |
guideline: 0.05..0.15 |
|
Diameter ratio |
d2/d2min with: |
guideline: 1.005..1.05 |
Ratio radius-width at outlet |
|
guideline: 1.005..1.05 |
Isentropic velocity ratio |
|
Reynolds number |
with d1 = highest diameter at inlet |
with b1 = width at inlet |
|
with d2 = highest diameter at outlet |
|
with b2 = width at outlet |
The guidelines given in the last column should be matched within the design.
It might be that for the chosen configuration of global setup and main dimensions a reasonable thermodynamic state cannot be calculated. This may be the case if e.g. the mass flow is too high for the chosen cross sections. Then a warning is generated.
The Meridional preview is based on the main dimensions designed until this point.
The Cordier diagram can be used for checking the impeller diameter d2.
See Cordier.
The Velocity triangles are the result of a mid-span calculation and are based on the design point and the main dimensions.
Problem |
Possible solutions |
|---|---|
Thermodynamic state cannot be calculated at inlet/outlet. Possible reason: choked flow. Consider change of main dimensions or global setup. |
|
The dimensions might be too tight for the specified mass flow and inlet conditions. In other words the mass flow is higher than the choked mass flow rate for the particular inlet condition and the respective cross section. |
Increase the dimensions (width, diameters etc.) or change the Global setup (e.g. decrease mass flow, increase pressure, decrease temperature). |
β1 differs by more than 25° from the flow imposed by the upstream component. |
|
β1 differs by more than 25° from β1mean. |
|
β1 differs by more than 25° from the flow imposed by the degree of reaction. |
|
The dimensions and the design point yield an estimated average relative inlet flow angle β1 that differs by more than 25° from the relative inlet flow angle imposed by the either of •swirl of the upstream component •β1mean •degree of reaction R see Setup. |
Change the dimensions (width, diameters etc.) or change the Global setup (e.g. mass flow, pressure ratio) or change inlet swirl in the Setup by either of parameters given on the left hand side. |